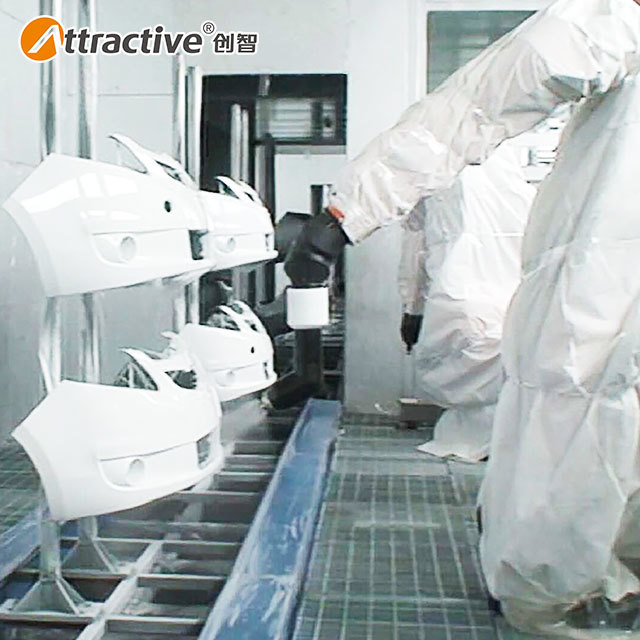
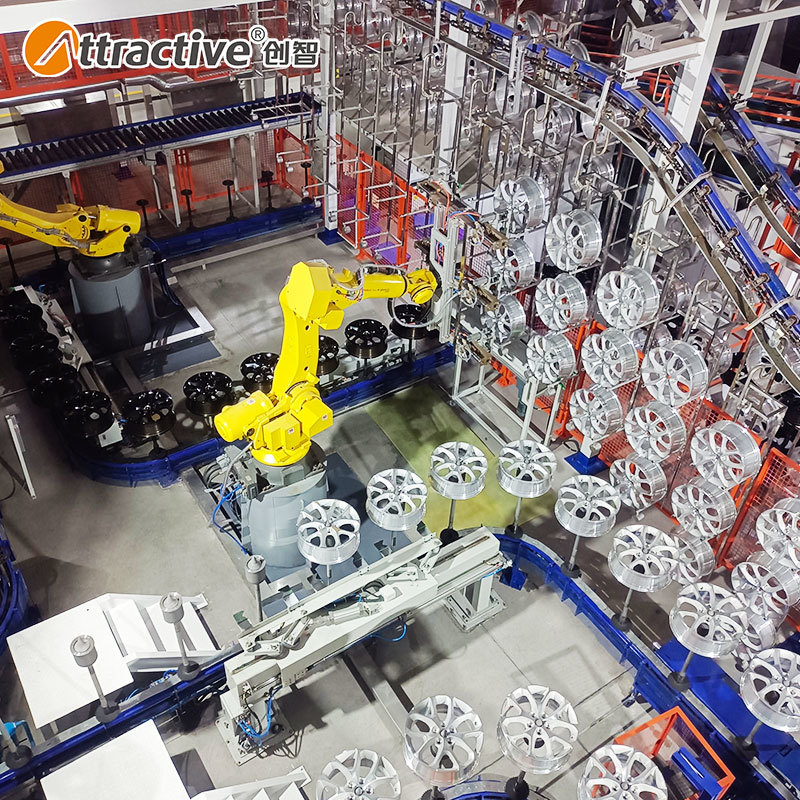
Related News
31
2025
-
07
Compliance Guide for Coating Line Construction Under 2025 VOCs Emission Regulations
Author:
Chuangzhi Coating
With increasingly stringent environmental policies, the 2025 VOCs emission regulations will be fully implemented, placing higher demands on the coating industry. How to avoid environmental "pitfalls" when building new coating lines and ensure smooth environmental impact assessment (EIA) acceptance has become a focus for enterprises. This article provides a comprehensive guide to avoiding these pitfalls.
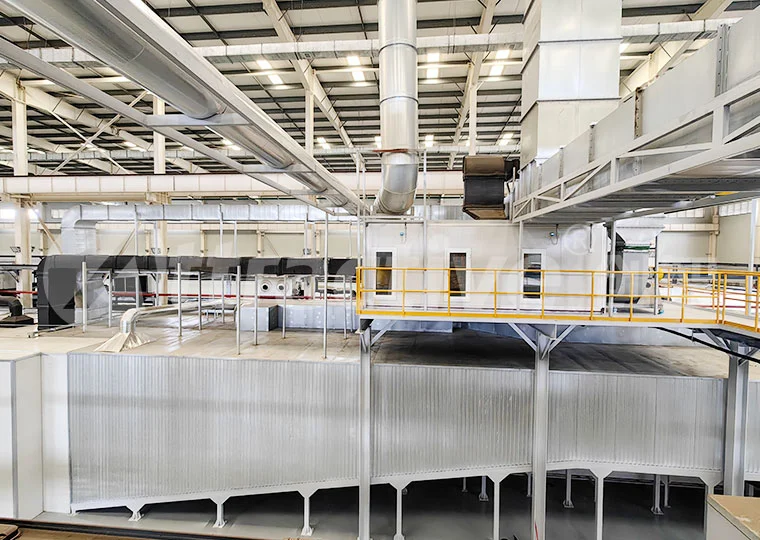

1. Interpretation of Core Requirements of the New Regulations
The 2025 VOCs emission regulations introduce significant changes in emission limits, monitoring requirements, and treatment technologies. Firstly, emission limits in key regions will be tightened by 30%-50%, with some sensitive areas even requiring "near-zero emissions." Secondly, the new regulations mandate the installation of online monitoring systems for real-time data upload to environmental supervision platforms. Thirdly, they explicitly require the adoption of an integrated treatment approach combining "source reduction + process control + end treatment," making single treatment technologies insufficient.
For the coating industry, the new regulations particularly emphasize the following: prohibition of high-VOCs coatings (exceeding 420g/L); spray booths must be enclosed and equipped with high-efficiency collection systems; exhaust gases from drying processes require separate treatment; and treatment facilities must achieve a removal efficiency of at least 80%.
2. Key Points in Coating Line Design
When designing new or retrofitted coating lines, the following aspects require special attention:
- Process Selection: Prioritize low-VOCs alternative technologies such as water-based coatings, powder coatings, or high-solid coatings. The design phase should consider future upgrades to meet environmental standards over the next 5-10 years.
- Equipment Selection: Spray booths must be fully enclosed with uniform airflow control systems (face velocity of 0.3-0.5m/s); drying ovens should use heat recovery technology to reduce energy consumption; conveyor systems should adopt energy-efficient designs.
- Exhaust Gas Collection: Adhere to the principle of "complete collection." Main pollution-generating sections such as spray booths, leveling rooms, and drying ovens must have independent collection systems. Pay special attention to collecting emissions from small, scattered points like paint mixing rooms and cleaning areas.
3. Comparison of VOCs Treatment Technologies
Current mainstream treatment technologies have distinct characteristics and should be selected based on actual enterprise conditions:
- Adsorption Concentration + Catalytic Combustion: Suitable for high-volume, low-concentration exhaust gases, with relatively low operating costs and removal efficiency exceeding 90%. However, attention must be paid to activated carbon replacement and disposal.
- RTO Regenerative Thermal Oxidation: High treatment efficiency (95%-99%), suitable for medium-to-high concentration exhaust gases, but with higher investment and operating costs. The new regulations require RTO thermal efficiency to be at least 95%.
- Biological Treatment: Applicable to specific VOCs components, with low operating costs but large footprint and relatively low treatment efficiency (70%-85%). Careful evaluation of applicability is needed.
- Combination Processes: Such as "adsorption + condensation recovery" or "scrubbing + photocatalytic oxidation," can provide customized solutions for complex exhaust gas components.
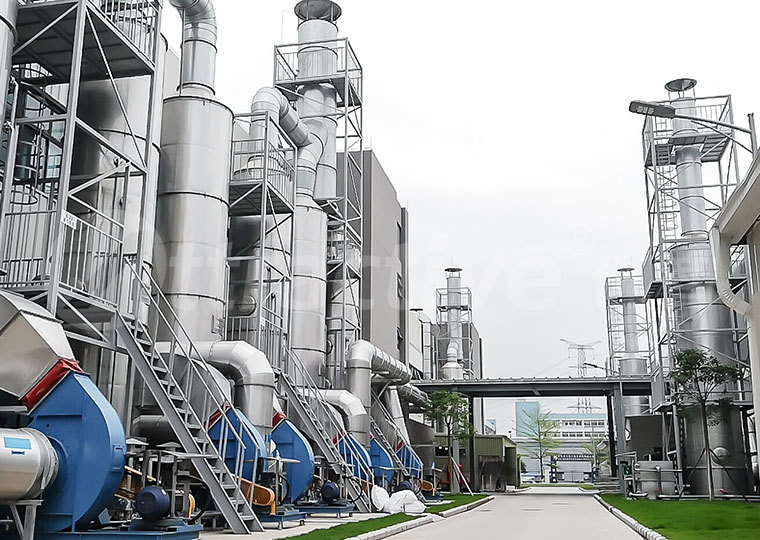

4. Key Points for EIA Acceptance
To ensure smooth EIA acceptance, note the following:
- Preparation: Avoid ecologically sensitive areas in site selection; communicate with environmental authorities in advance to understand local special requirements; commission professional agencies to prepare EIA reports.
- Process Management: Strictly follow EIA requirements during construction; maintain complete records of equipment procurement, installation, and commissioning; establish standardized environmental management systems.
- Acceptance Testing: Engage qualified third-party testing; ensure production load reaches at least 75%; comply with specified monitoring frequency and duration; prepare complete operation logs.
5. Long-Term Compliance Recommendations
Achieving sustained compliance requires establishing long-term mechanisms:
- Daily Management: Designate dedicated environmental management personnel; maintain operation logs for treatment facilities; conduct regular testing and equipment maintenance; retain monitoring records for at least 3 years.
- Technology Upgrades: Stay informed about industry technological advancements; reserve 10%-20% additional treatment capacity; evaluate technology applicability every 3-5 years.
- Emergency Preparedness: Develop emergency response plans for environmental incidents; stock critical spare parts; conduct regular drills; establish partnerships with professional environmental companies.
Conclusion
Facing the 2025 VOCs emission regulations, coating enterprises must plan ahead, design scientifically, and operate standardly to avoid environmental penalty risks. Choosing professional and reliable environmental protection equipment suppliers is crucial for ensuring compliant operation of coating lines.
SEO: