Related News
27
2025
-
02
How to Choose the Right Paint Booth for Your Coating Line?
Author:
Chuangzhi Coating
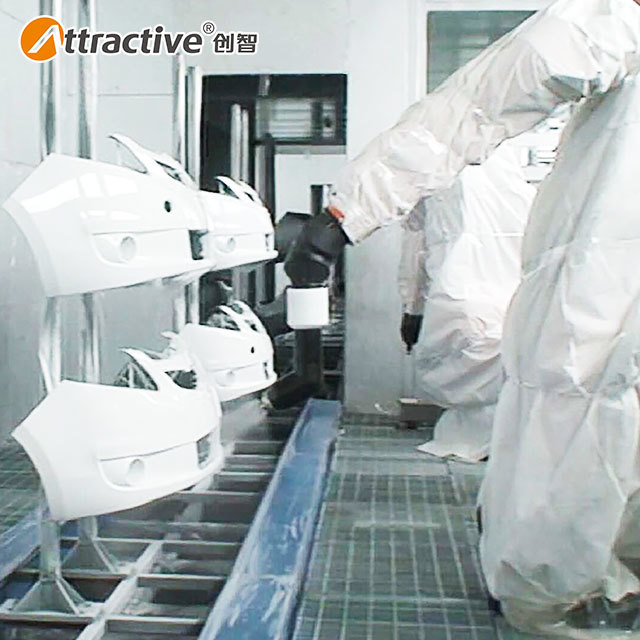
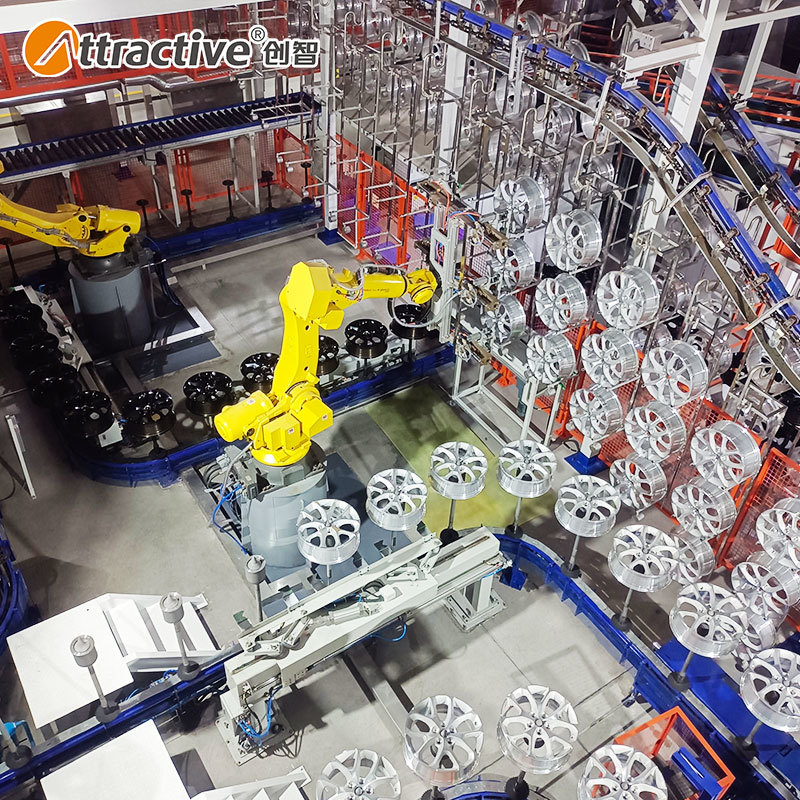
The paint booth is a critical component of any coating line, directly impacting coating quality, production efficiency, and environmental compliance. However, with various types available—dry filter, water wash, side draft, downdraft—selecting the right booth can be challenging. This guide explores booth types, sizing, ventilation systems, and energy-saving technologies, supported by industry data and real-world cases, to help you make an informed decision.
1. Paint Booth Types: Dry Filter vs. Water Wash
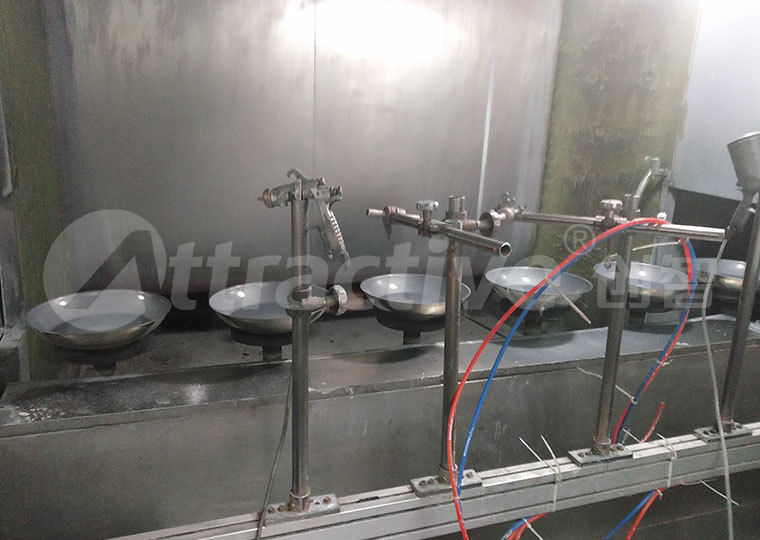
Dry Filter Booth
How It Works: Captures overspray using multi-layer filter media (e.g., fiberglass, paper), with exhaust treated by activated carbon.
Key Advantages:
- Lower Initial Cost: No water circulation system required.
- Energy Efficiency: 30-40% less energy consumption than water wash booths.
- Ideal For: Small-batch production, repair shops, wood coating.
Limitations:
- Frequent filter replacement (every 200 hours) increases long-term costs.
- Less effective for high-viscosity materials (e.g., putty).
Case Study: After a furniture manufacturer adopted a dry spray paint room, the initial investment saved 150,000 CNY, but the annual consumables cost increased by 30,000 CNY.

Water Wash Booth
How It Works: Uses water curtains or cyclonic systems to trap overspray, with water recycled after treatment.
Key Advantages:
- High Efficiency: 95%+ overspray capture, suitable for high-volume production.
- Lower Long-Term Costs: No filter replacements; water is reusable.
- Ideal For: Automotive manufacturing, metal coating, continuous operations.
Limitations:
- 40-60% higher initial cost due to water treatment systems.
- Requires antifreeze measures in cold climates.
Industry Data: 85% of automotive paint booths use water wash systems (China Coating Equipment Market Report).

2. Sizing Your Paint Booth: 5 Critical Parameters
Workpiece Dimensions: Booth width = Max workpiece width + 1.5 m (operating space).
Airflow Velocity:
- Dry booth: 0.3-0.5 m/s
- Water wash booth: 0.25-0.35 m/s
Lighting: ≥800 Lux (LED explosion-proof lights).
Door Height: Workpiece height + 0.8 m (clearance for handling).
Exhaust Capacity: 60-120 air changes per hour (adjust based on VOC levels).
Design Mistake Alert: A machinery manufacturer lost $70,000 due to inadequate robot arm clearance.
3. Ventilation Systems: Balancing Efficiency and Energy Use
Downdraft Design
- Vertical airflow from ceiling to floor, ideal for high-precision coating (e.g., automotive topcoats).
- Energy use: 20% higher than side draft but improves consistency by 35%.
Venturi Water Curtain
- Uses V-shaped plates to create negative pressure, with 92% overspray capture efficiency.
VOC Treatment
- Activated carbon + RTO: 99% efficiency but energy-intensive.
- Zeolite rotor concentrators: 40% lower energy use for low-concentration VOCs.
4. Energy-Saving Technologies: Cut Costs by 30%
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) Fans
- Adjust fan speed based on spraying volume, reducing electricity use by 25-35%.
- Case: An appliance manufacturer cut annual energy costs from 17,000.
Heat Recovery Systems
- Reuse oven waste heat to preheat fresh air, ideal for regions with average temperatures below 15°C.
LED Lighting
- 60% less energy than metal halide lights, with 50,000-hour lifespan.
Smart Monitoring
- Track energy use, VOC emissions, and equipment health for predictive maintenance.
5. Decision-Making Flowchart
Define Needs: Production volume, coating type (water-based/solvent), budget.
Select Type:
- Small batch → Dry filter
- High volume → Water wash
Calculate Size: Workpiece dimensions + safety margins.
Choose Ventilation: Downdraft for precision, side draft for general use.
Add Energy Savings: Prioritize VFD fans and heat recovery if budget allows.
Industry Trends: 2024 Paint Booth Innovations
Modular Design: Quick assembly for flexible production.
Zero-Emission Tech: Combine RTO with carbon capture for near-zero VOC emissions.
AI-Driven Optimization: Auto-adjust airflow and overspray handling via vision systems.