Related News
26
2025
-
02
The Future of UV Curing in Industrial Coating Processes: Advantages, Applications, and Challenges
Author:
Chuangzhi Coating
In the industrial coating sector, efficiency and environmental sustainability have become critical competitive factors. UV curing technology (ultraviolet curing), with its unique advantages, is gradually replacing traditional thermal curing processes and gaining traction in industries such as automotive, electronics, woodworking, and packaging. This article explores the core benefits, applications, and comparisons of UV curing with conventional methods, while forecasting future trends.
Core Advantages of UV Curing Technology
- Instant Curing, Enhanced Efficiency
UV curing completes in seconds to minutes, compared to thermal curing (typically 30 minutes to several hours), boosting production efficiency by over 90%. - Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- 70%+ energy savings: UV curing requires no high-temperature ovens, only UV light sources.
- Zero VOC emissions: UV coatings contain no volatile organic solvents, complying with global regulations (e.g., EU REACH).
- 70%+ energy savings: UV curing requires no high-temperature ovens, only UV light sources.
- Superior Coating Performance
- High hardness and wear resistance: UV coatings achieve hardness levels above 4H (traditional coatings: 2H).
- Chemical resistance: Ideal for automotive interiors and electronics requiring corrosion resistance.
- High hardness and wear resistance: UV coatings achieve hardness levels above 4H (traditional coatings: 2H).
- Precision Processing
UV light enables localized or 3D surface curing, minimizing material waste.

Applications of UV Curing
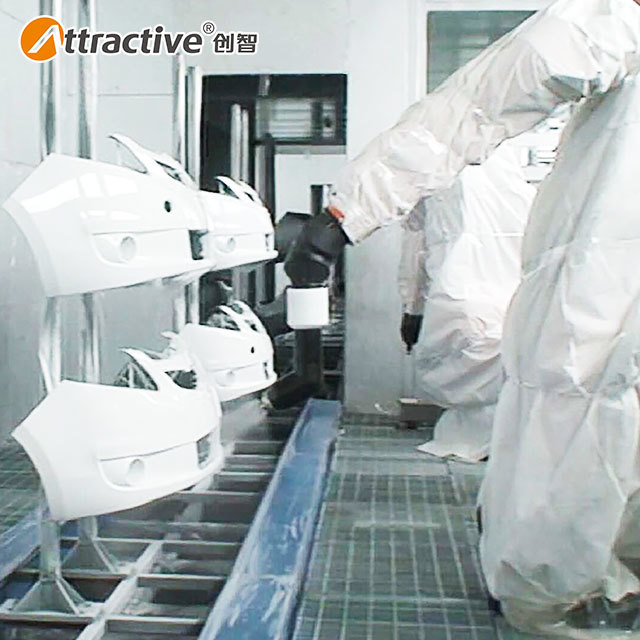
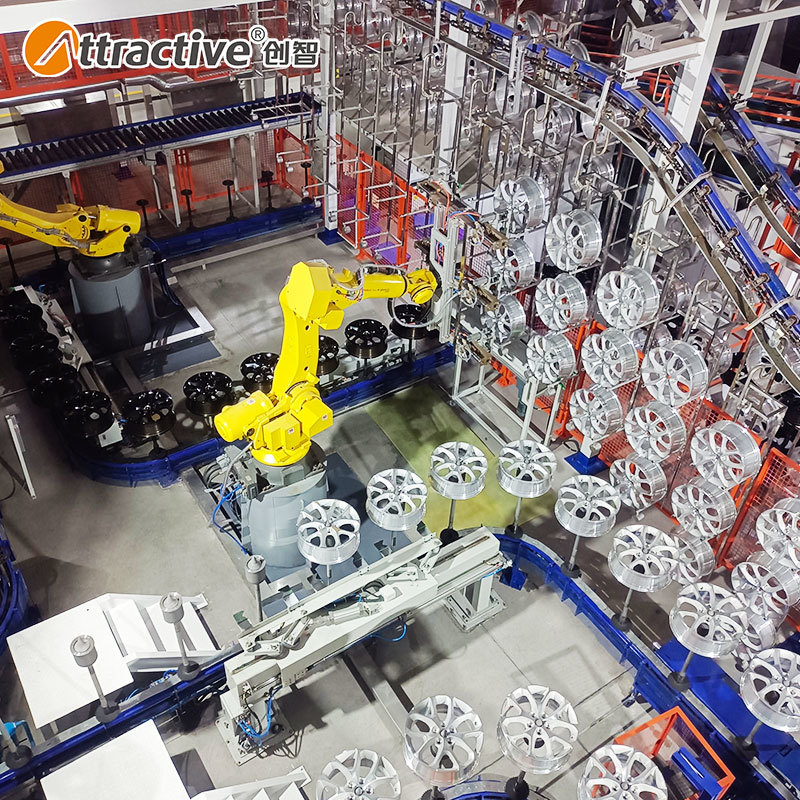
- Automotive Industry
- Interior components: Matte or glossy coatings for dashboards and consoles.
- Headlight lens hardening: Improved light transmission and anti-aging properties.
- Interior components: Matte or glossy coatings for dashboards and consoles.
- Consumer Electronics
- Anti-fingerprint coatings for smartphone casings and laptops.
- Rapid curing of circuit board insulating layers.
- Anti-fingerprint coatings for smartphone casings and laptops.
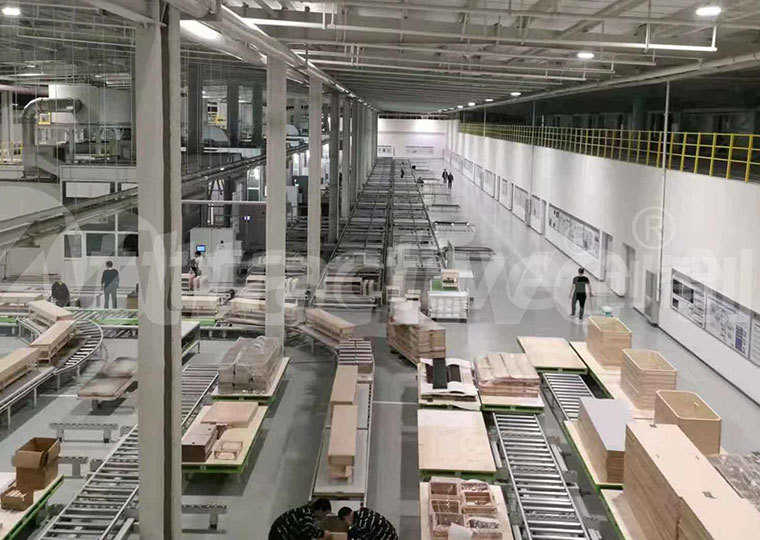
- Wood Coating
- “Instant” curing of furniture primers, shortening production cycles.
- Scratch-resistant and anti-yellowing treatments for flooring.
- “Instant” curing of furniture primers, shortening production cycles.
- Packaging Printing
- Eco-friendly UV inks for food packaging, eliminating solvent residues.
- Eco-friendly UV inks for food packaging, eliminating solvent residues.
UV Curing vs. Thermal Curing: Key Comparisons
Metric | UV Curing | Thermal Curing |
|---|---|---|
Curing Time | 5-30 seconds | 30 minutes-2 hours |
Energy Use | Low (UV lamps only) | High (heating to 120-200°C) |
Eco-Friendliness | Zero VOCs | VOC emissions requiring treatment |
Material Compatibility | Plastics, metals, wood | High-temperature metals, ceramics |
Initial Cost | Higher (UV lamps, optics) | Lower |
Challenges and Future Trends
Challenges
- Material limitations: UV-specific coatings cost 20-30% more than traditional paints.
- Equipment costs: High initial investment for UV lamps and optical systems.
- Complex geometry curing: Deep cavities or multi-layer parts may require multiple exposures.
Future Directions
- Hybrid Curing: Combine UV and thermal curing for thick metal coatings.
- LED UV Adoption: Longer lifespan (20,000+ hours), lower energy use, and mercury-free.
- Smart Integration: AI-driven optimization of light intensity and paths for adaptive curing.
- Bio-Based UV Coatings: Renewable raw materials to reduce carbon footprint.
Industry Cases:
- A German automaker: Reduced energy use by 40% and CO₂ emissions by 120 tons/year using UV-LED for door handle coatings.
- A Japanese electronics firm: Achieved customizable smartphone textures with UV-cured 3D printing.

Why UV Curing Will Dominate Industrial Coating
Driven by global carbon neutrality goals, UV curing is reshaping industrial coating with its efficiency, sustainability, and performance. Despite higher upfront costs, long-term savings in energy, labor, and environmental compliance deliver significant ROI. The global UV curing market is projected to exceed $8 billion by 2030, growing at 9.2% annually.
Contact us now for more details!